Laser cutting & Engraving Technologies
Vaporization cutting #
In vaporization cutting the focused beam heats the surface of the material to boiling point and generates a keyhole.
The keyhole leads to a sudden increase in absorptivity quickly deepening the hole.
As the hole deepens and the material boils, vapor generated erodes the molten walls blowing ejecta out and further enlarging the hole.
Non melting material such as wood, carbon and thermoset plastics are usually cut by this method.

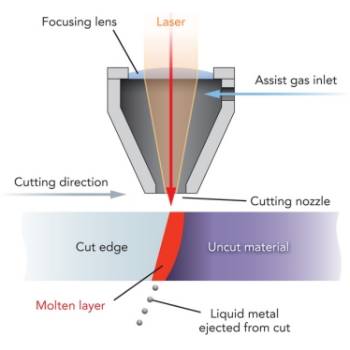
Melt and blow #
Melt and blow or fusion cutting uses high-pressure gas to blow molten material from the cutting area, greatly decreasing the power requirement.
First the material is heated to melting point then a gas jet blows the molten material out of the kerf avoiding the need to raise the temperature of the material any further.
Materials cut with this process are usually metals.
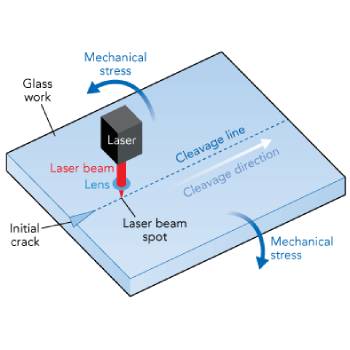
Thermal stress cleavage #
The full body cleavage is formed at the position where the stress intensity factor takes the maximum value.
This position usually does not coincide with the spot where the temperature becomes maximum, generating what is called size effect.
This size effect is avoided by converting the direction of work distortion accompanying full body cleavage to be perpendicular to the work surface.
The case of surface scribing is much simpler but needs a cooling unit placed immediately after the end of work heating.
Because the present business competition is mostly performed using the technology of surface scribing, the competition is mostly being made to improve the capability of surface scribing technology.
http://www.industrial-lasers.com/articles/2011/11/thermal-stress-cleavage-is-a-new-business.html
Stealth dicing of silicon #
The separation of microelectronic chips as prepared in semiconductor device fabrication from silicon wafers may be performed by the so-called stealth dicing process, which operates with a pulsed Nd:YAG laser, the wavelength of which is well adopted to the electronic band gap of silicon.
![]()
Reactive Laser cutting #
Also called “burning stabilized laser gas cutting”, “flame cutting”. Reactive cutting is like oxygen torch cutting but with a laser beam as the ignition source. Mostly used for cutting carbon steel in thicknesses over 1 mm.
This process can be used to cut very thick steel plates with relatively little laser power.
